Foxglove WebRTC
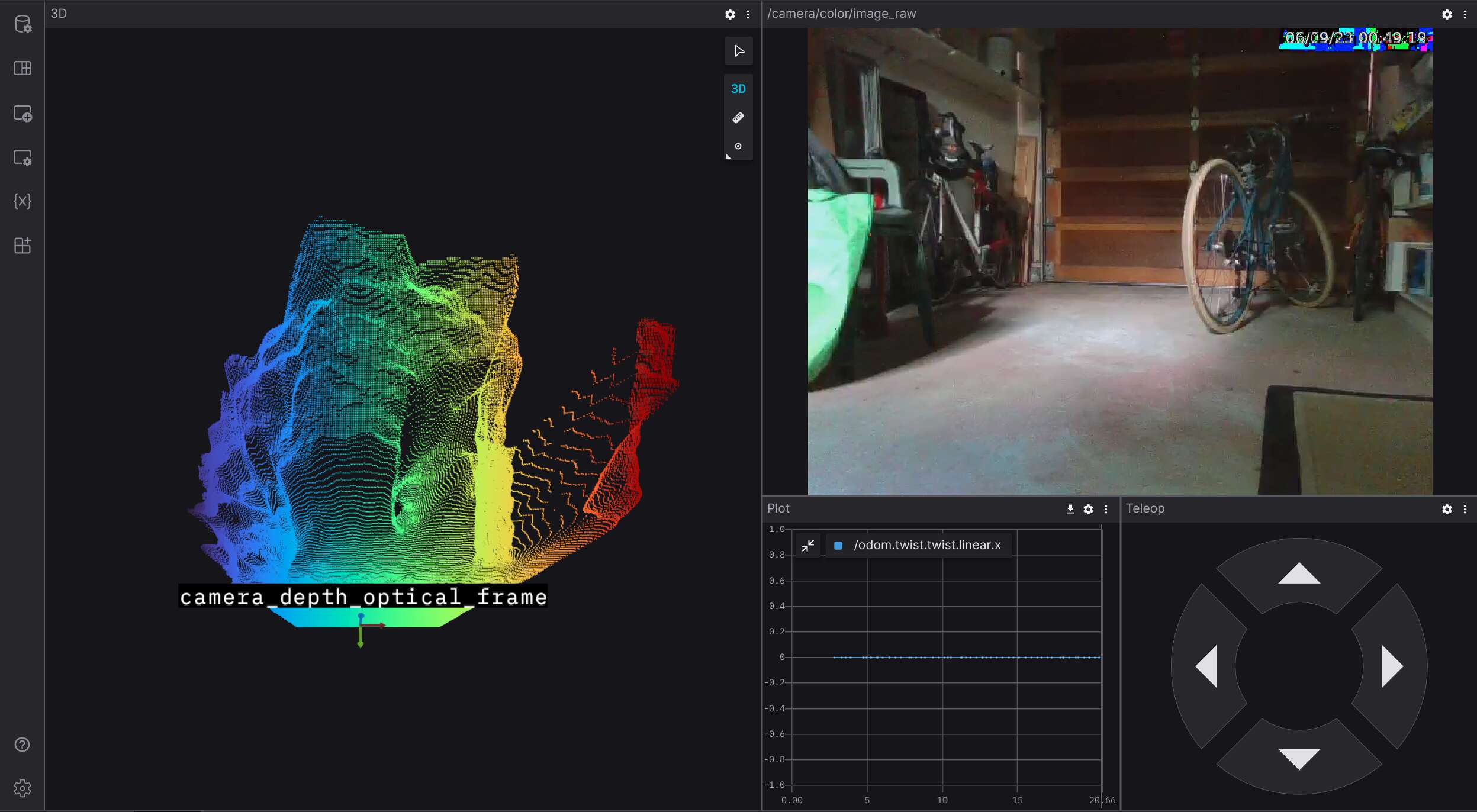
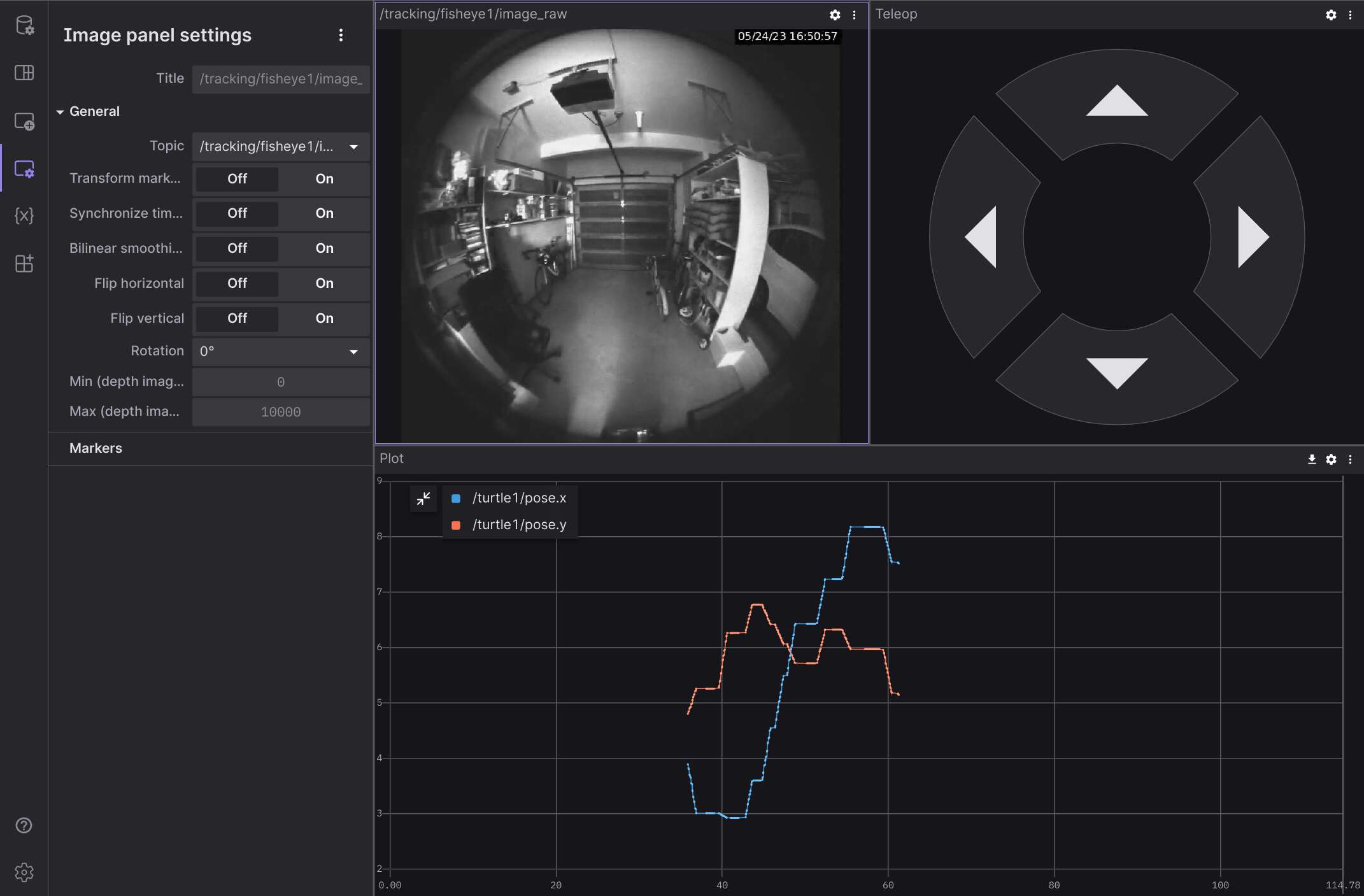
Makes it trivial to see a robot live in Foxglove — efficiently, and no matter where the robot is or how it is connected to the Internet. This is accomplished by using the WebRTC Video capability to create a direct, peer-to-peer WebRTC connection between the browser and the robot.
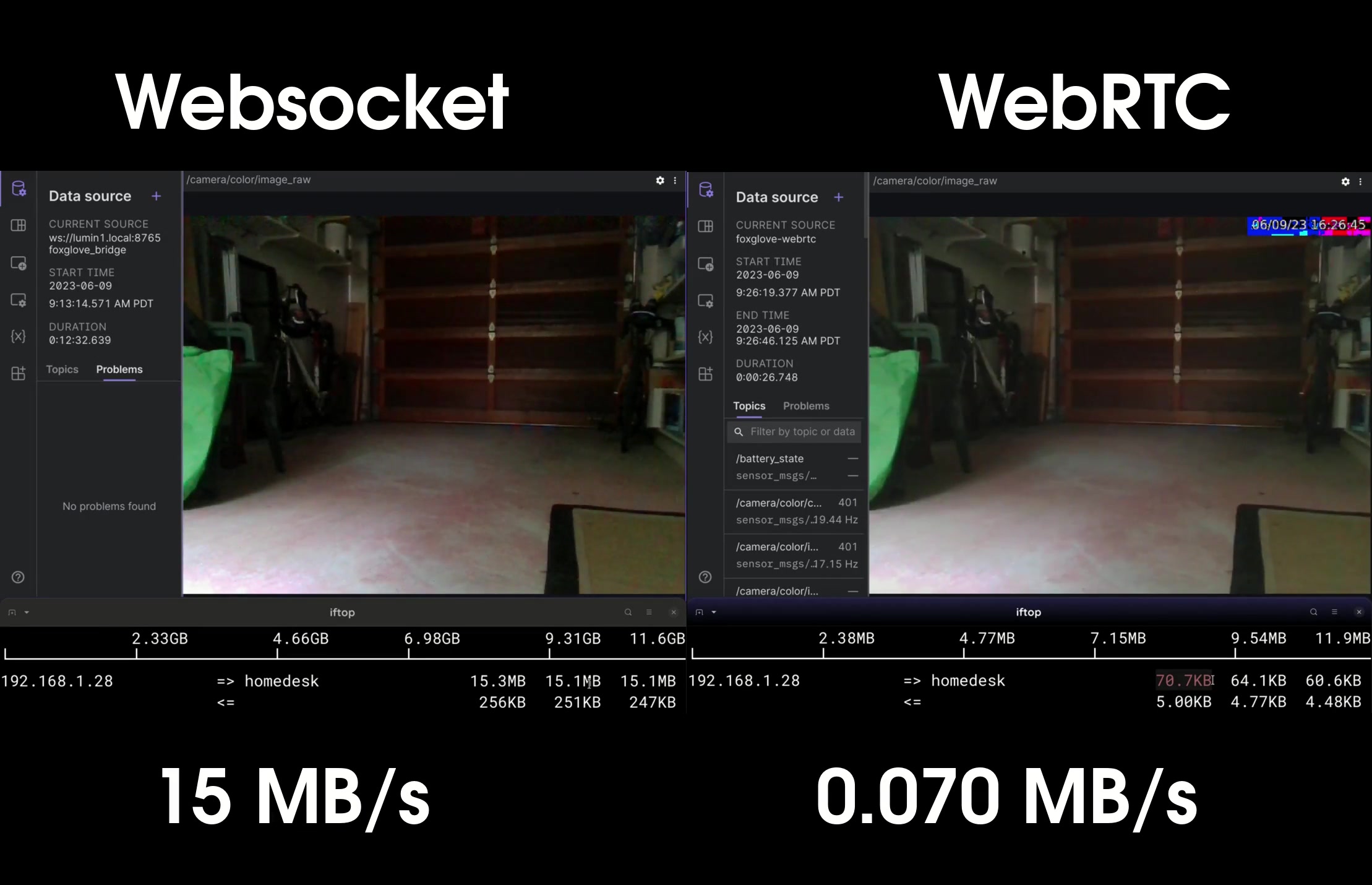
For robots deployed in the field the use of WebRTC is ideal. Besides solving the problem of firewalls and NATs, WebRTC also enables much higher efficiency for streaming ROS image topics. Rather than sending individual images, this capability uses H264 video compression to transmit the stream orders of magnitude more efficiently. It also provides congestion control (dynamically reducing video encoding bitrate when bandwidth dips) and efficiently handles packet loss. Non-image topics are transmitted via a data-channel provided by the same, efficient WebRTC connection.
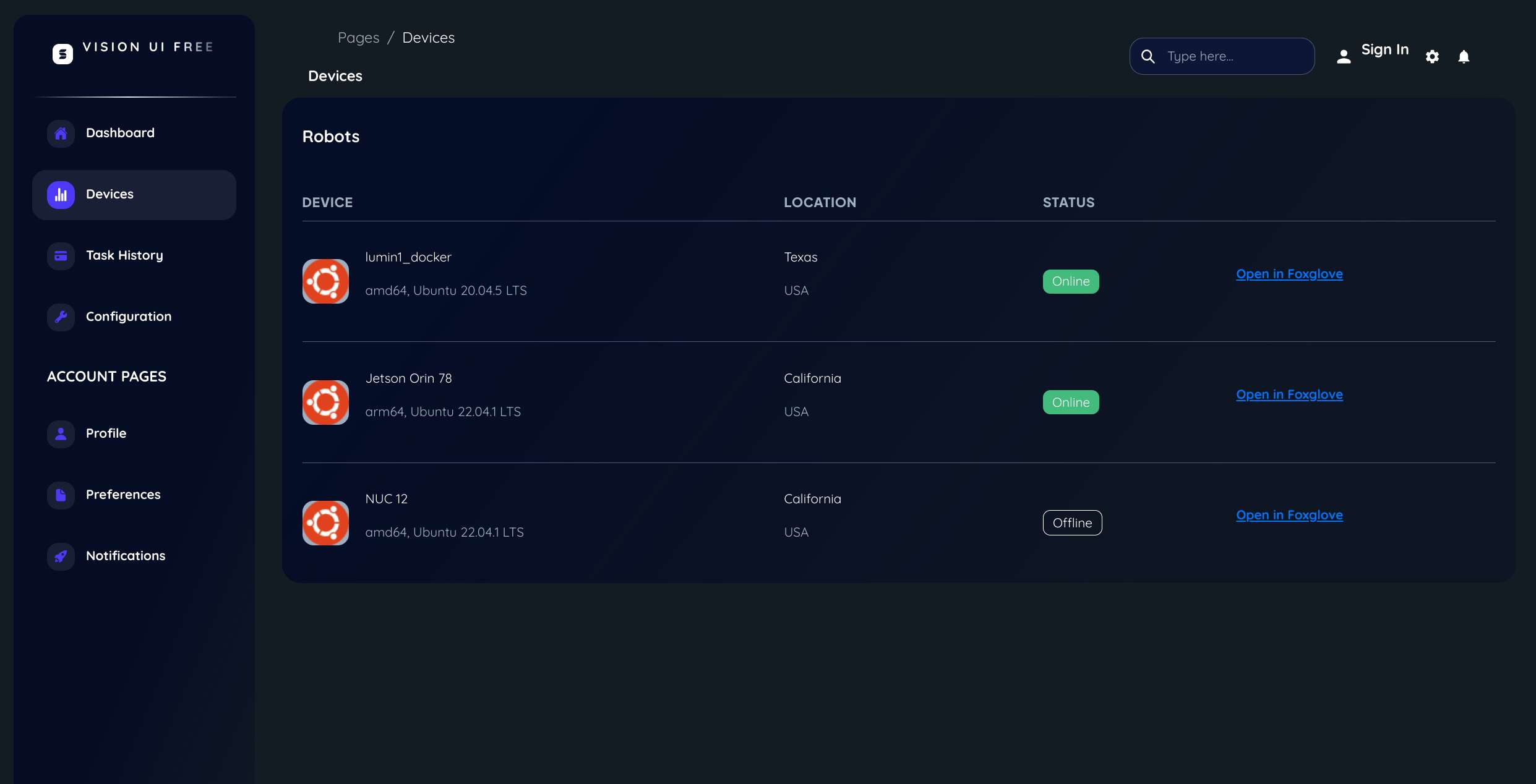
The capability provides a link for each robot in your fleet. That link opens Foxglove with all the necessary connection and authentication parameters to see that robot. This effectively turns Foxglove into a fleet monitoring tool without the need to set up and maintain your own VPN or cloud proxy to connect to your robots.
New in 0.6
- Improved congestion control (see webrtc-video 0.17 for details).
New in 0.5
- ROS 2 support
- specify bandwidth limits for video-streams and other topics
- this prevents issues when a user subscribes to very large topics, such as pointclouds
- support for bayer-encoded image topics